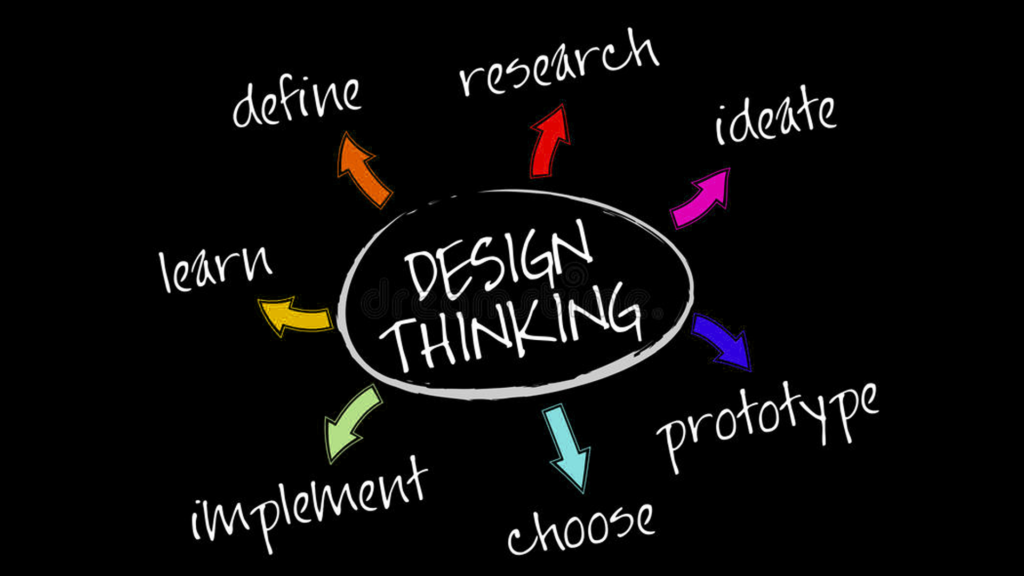
Design Thinking is a creative problem-solving process that focuses on the needs of the end user. It is a human-centered approach that involves empathy, experimentation, and collaboration to generate innovative solutions to complex problems.
The design thinking process typically consists of five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. In the empathize phase, designers seek to understand the needs, motivations, and emotions of the end users through research and observation. In the define phase, designers identify the problem they want to solve and articulate a clear and specific design challenge. In the ideate phase, designers generate a wide range of potential solutions to the design challenge through brainstorming and other creative techniques. In the prototype phase, designers create a tangible representation of their ideas to test and refine them. Finally, in the test phase, designers gather feedback from users and iterate on their prototypes based on that feedback.
Design thinking has its roots in the fields of design and engineering, but it has since been adopted by a wide range of industries, including healthcare, education, and business. It is often used to develop new products, services, and experiences that are user-friendly, effective, and visually appealing.
One of the key benefits of design thinking is its focus on empathy and user-centeredness. By putting the needs of the end user at the center of the design process, designers are able to create solutions that are more relevant, useful, and desirable to users. This focus on the user also helps designers avoid common pitfalls, such as designing for themselves or creating solutions that do not solve the underlying problem.
Another benefit of design thinking is its emphasis on experimentation and iteration. By rapidly prototyping and testing their ideas, designers are able to quickly identify what works and what doesn’t, and make necessary adjustments to improve their designs. This iterative approach allows designers to be agile and flexible, and to quickly respond to changing user needs and market conditions.
Design thinking also promotes collaboration and co-creation, as it encourages designers to work together and incorporate diverse perspectives into the design process. By bringing together a team of designers with different backgrounds and skills, designers are able to generate more diverse and creative ideas, and benefit from each other’s expertise and insights.
Overall, design thinking is a powerful tool for generating innovative solutions to complex problems. By applying the principles of empathy, experimentation, and collaboration, designers are able to create user-centered designs that are relevant, effective, and desirable.